

This lab focuses on implementing and analyzing SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) and FTP (File Transfer Protocol) in Cisco Packet Tracer, along with network traffic analysis using Wireshark for various protocols including HTTP/HTTPS, DNS, TCP, and UDP.
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is an Internet standard for electronic mail (email) transmission. First defined by RFC 821 in 1982, it was last updated in 2008 with Extended SMTP additions by RFC 5321.
# SMTP Key Points:
- Mail servers use port 25 for communication
- Clients typically use port 587 for submission
- Uses TCP for reliable delivery
- Works with POP3/IMAP for receiving emails
- Commands: HELO, MAIL FROM, RCPT TO, DATA, QUIT
Topology Setup and Configuration:
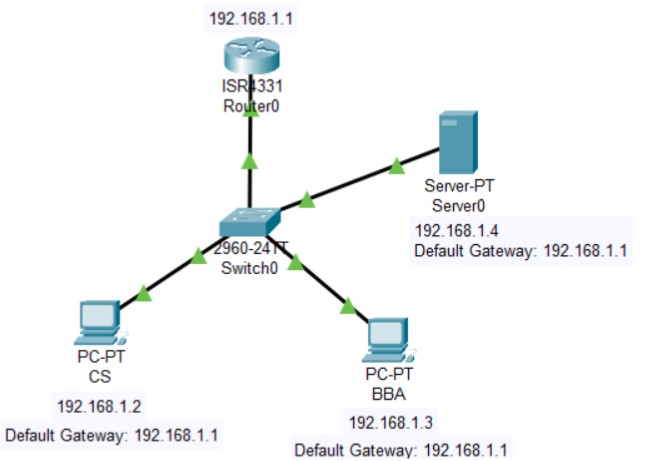
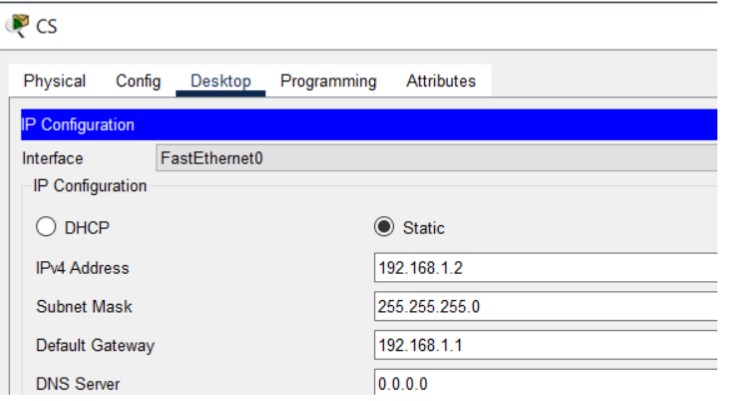
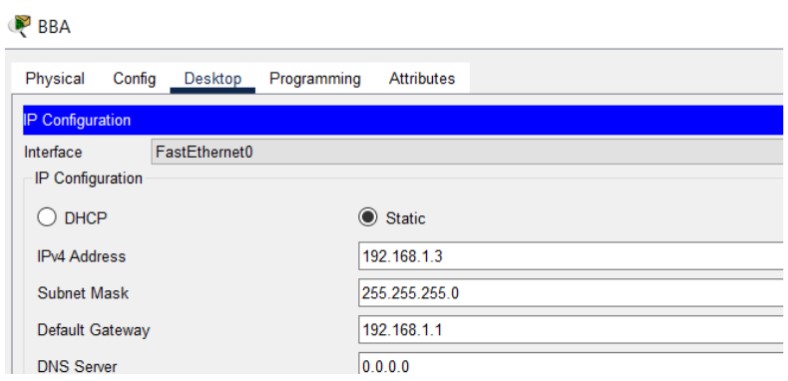
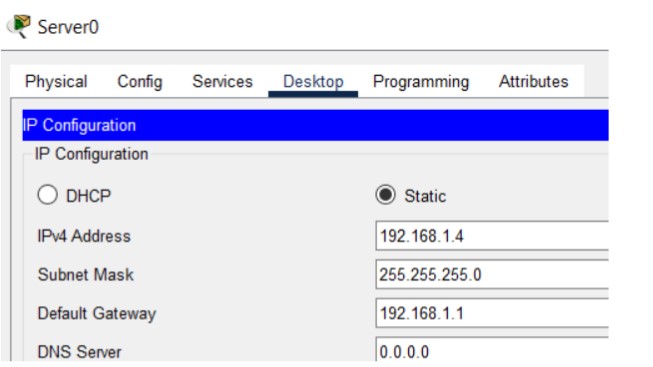
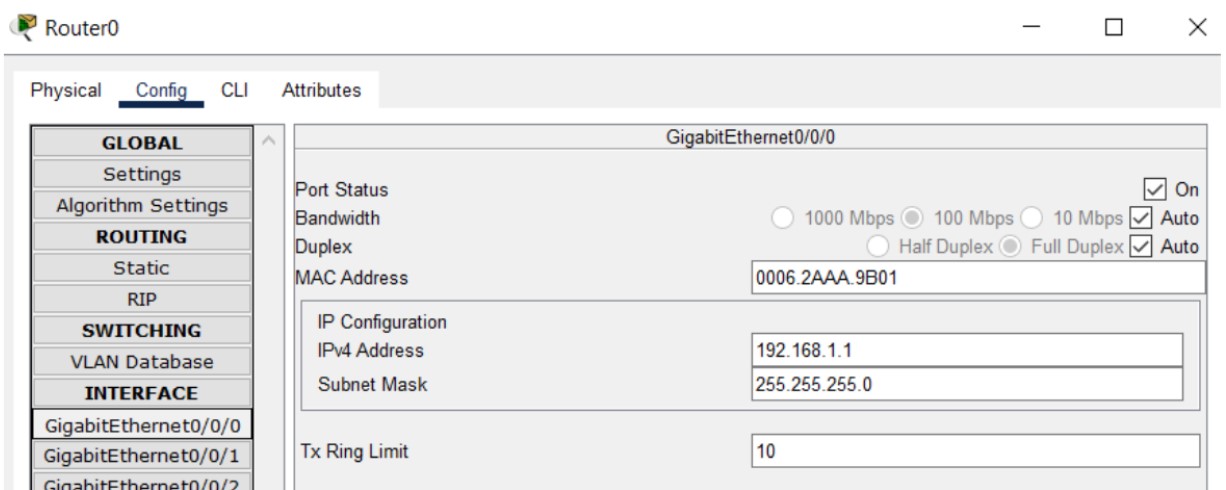
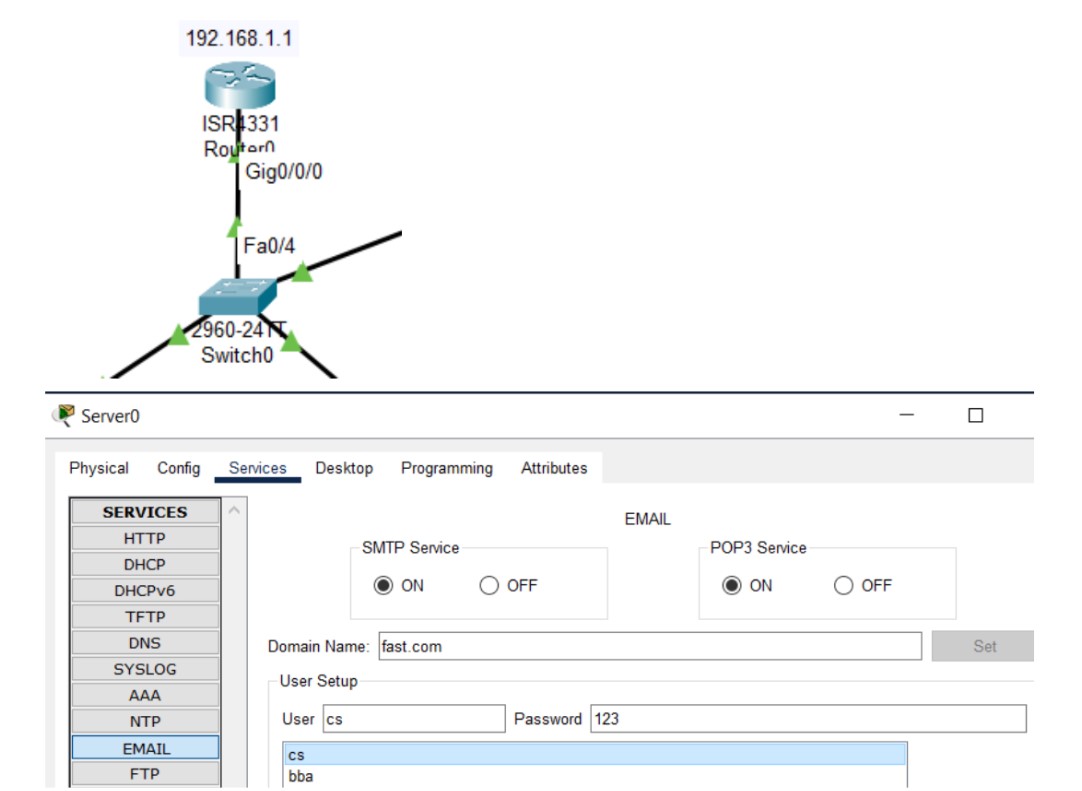
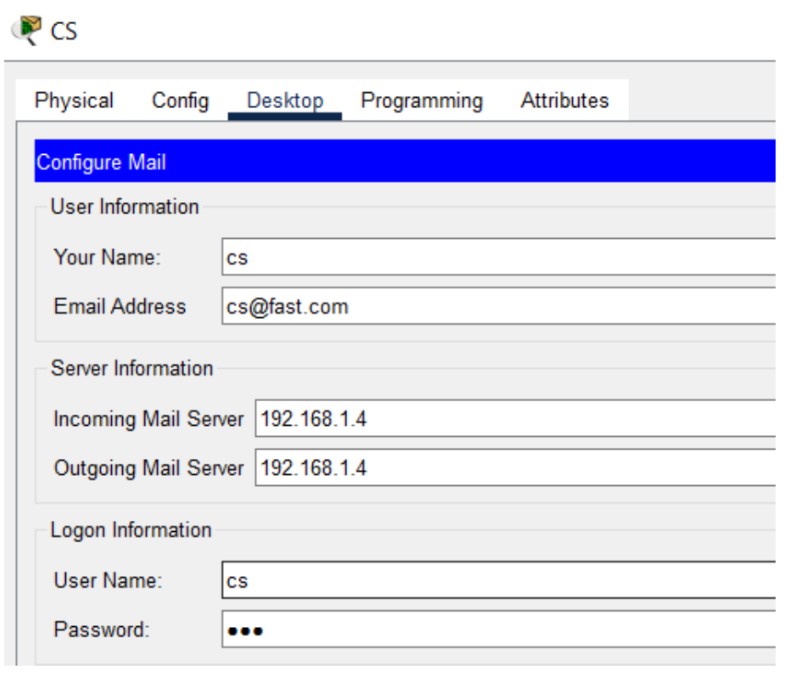
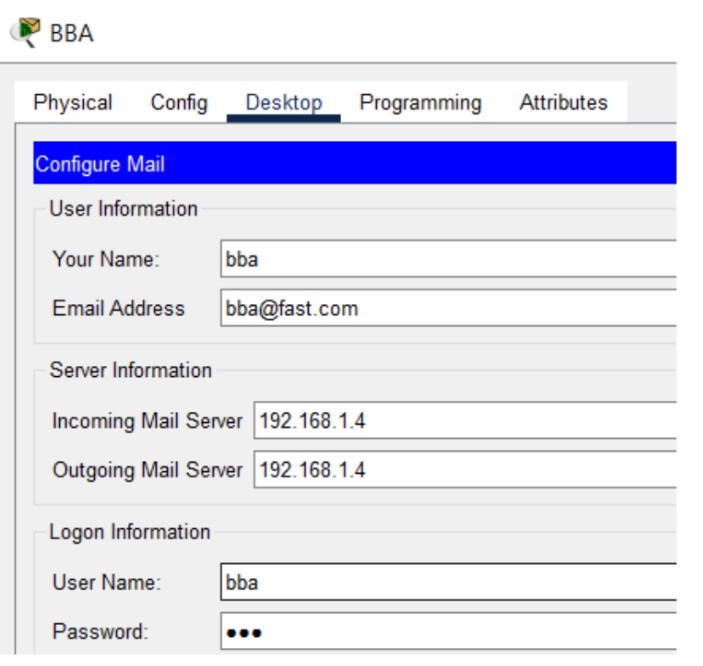
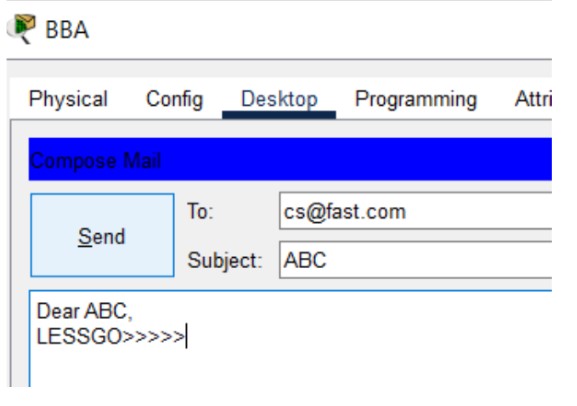
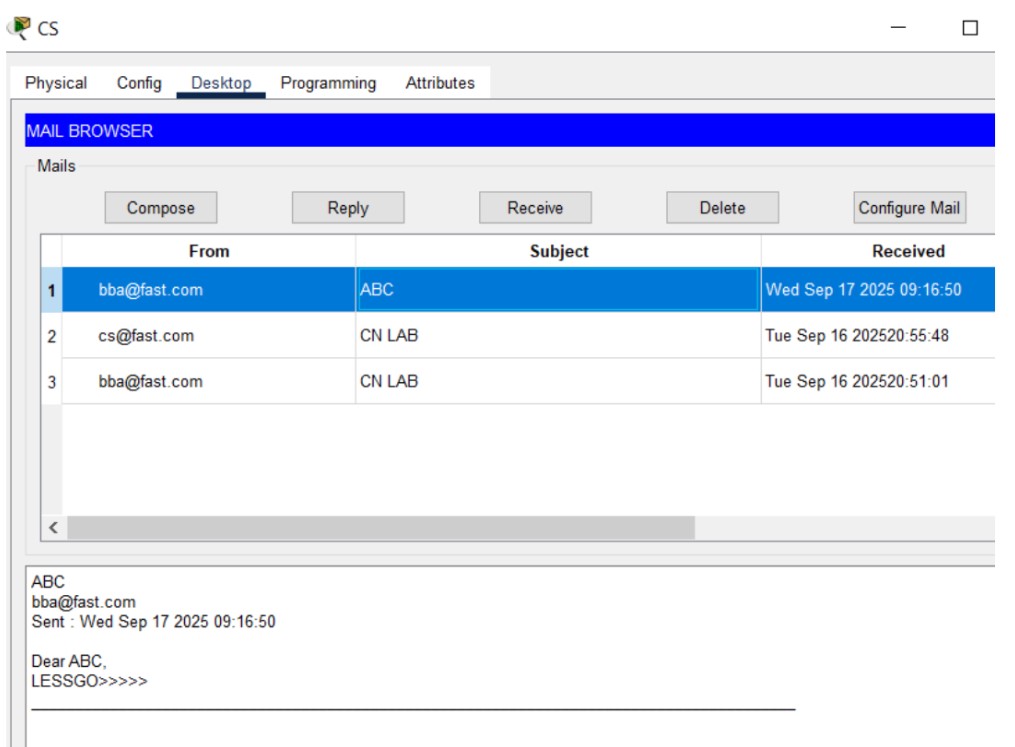
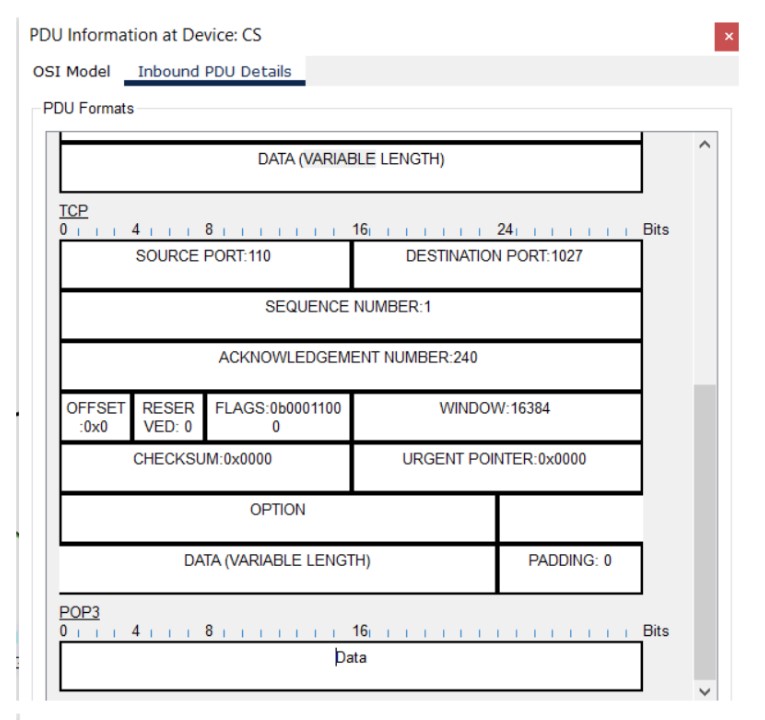
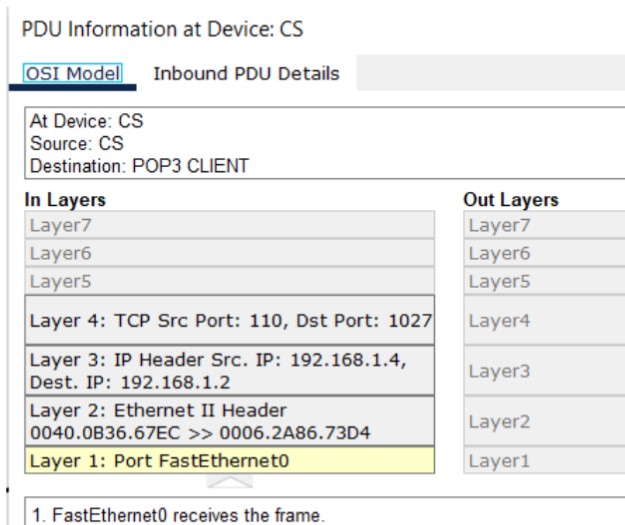
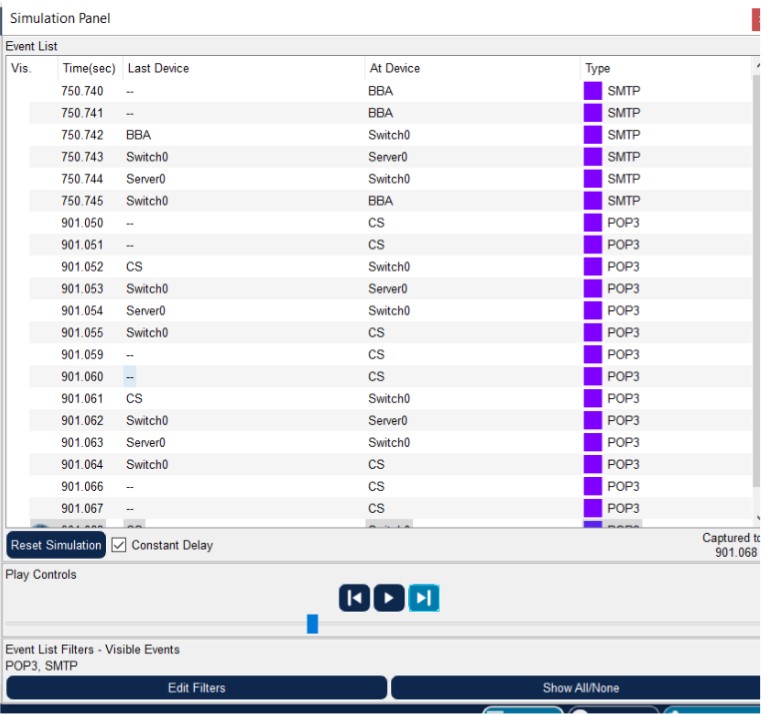
Figure 1: SMTP implementation network topology with mail server and client PCs.
| Username | Password |
|---|---|
| cs | 123 |
| bba | 123 |
The File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard network protocol used to transfer computer files between a client and server on a computer network. FTP uses separate control and data connections.
# FTP Key Points:
- Control connection: Port 21
- Data connection: Port 20 (active mode)
- Uses TCP for reliability
- Supports active and passive modes
- Commands: USER, PASS, LIST, RETR, STOR, QUIT
Topology Setup and Configuration:
Let's implement FTP Service on the same topology as above.
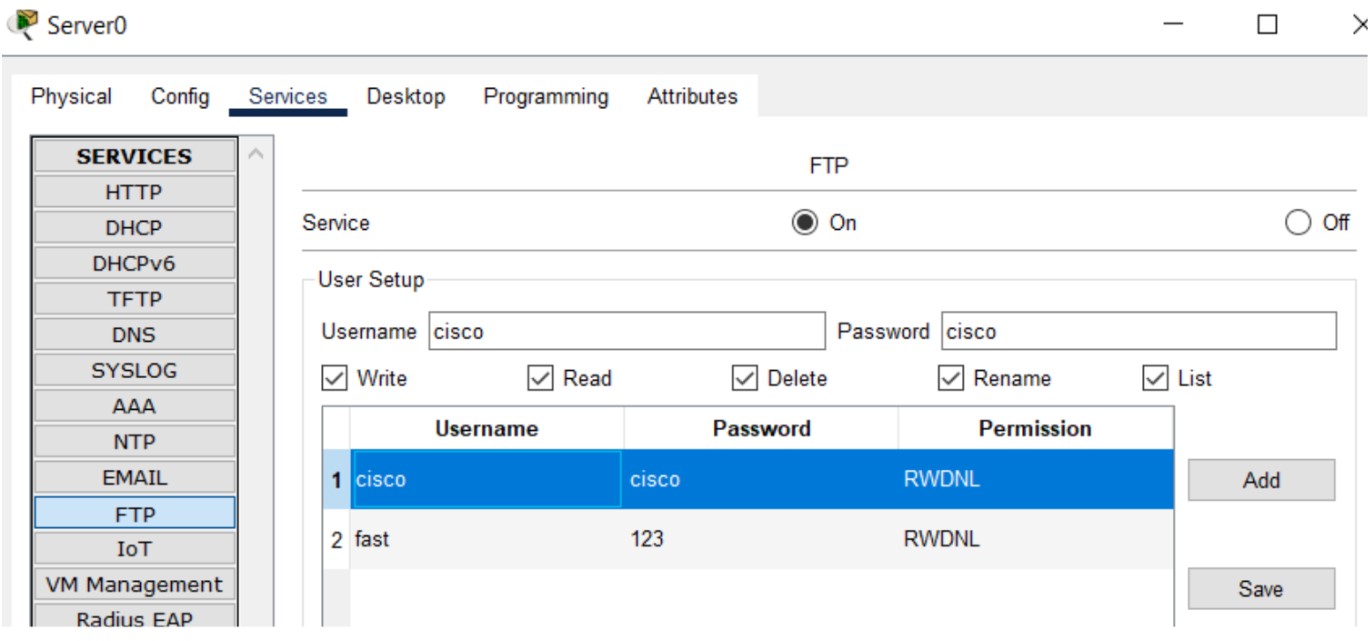
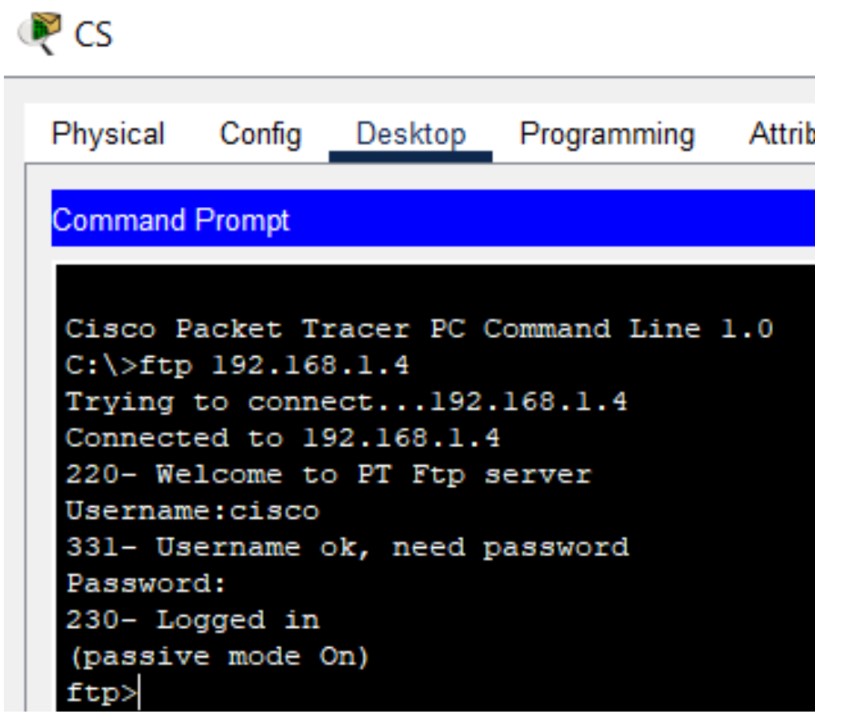
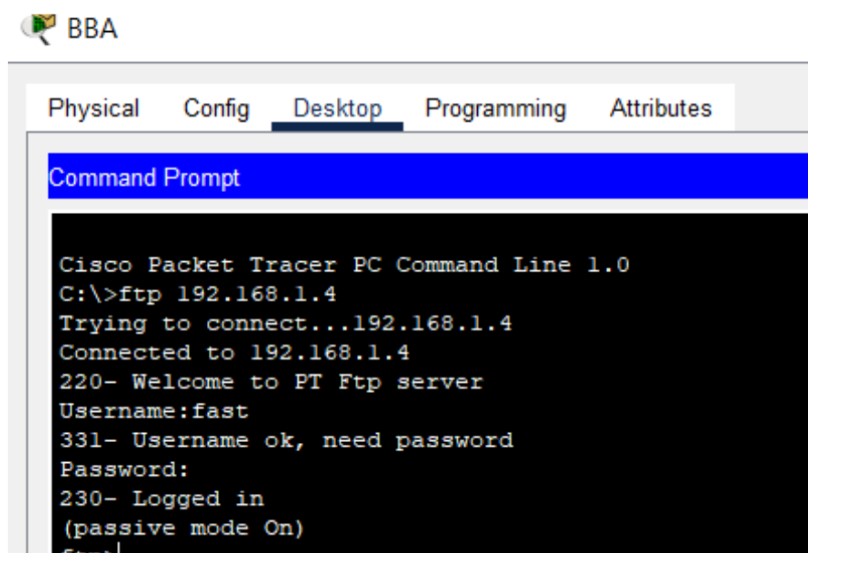
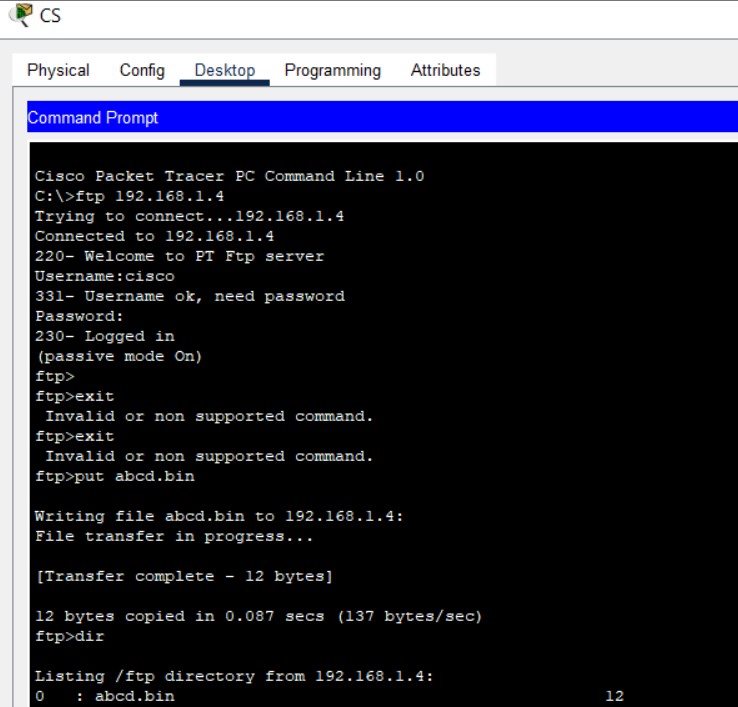
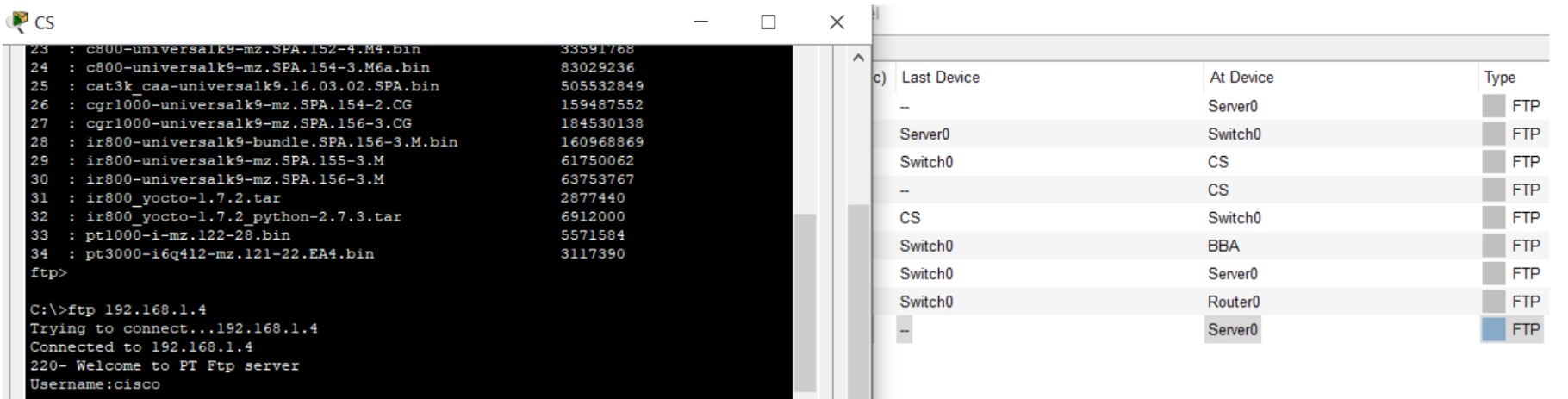
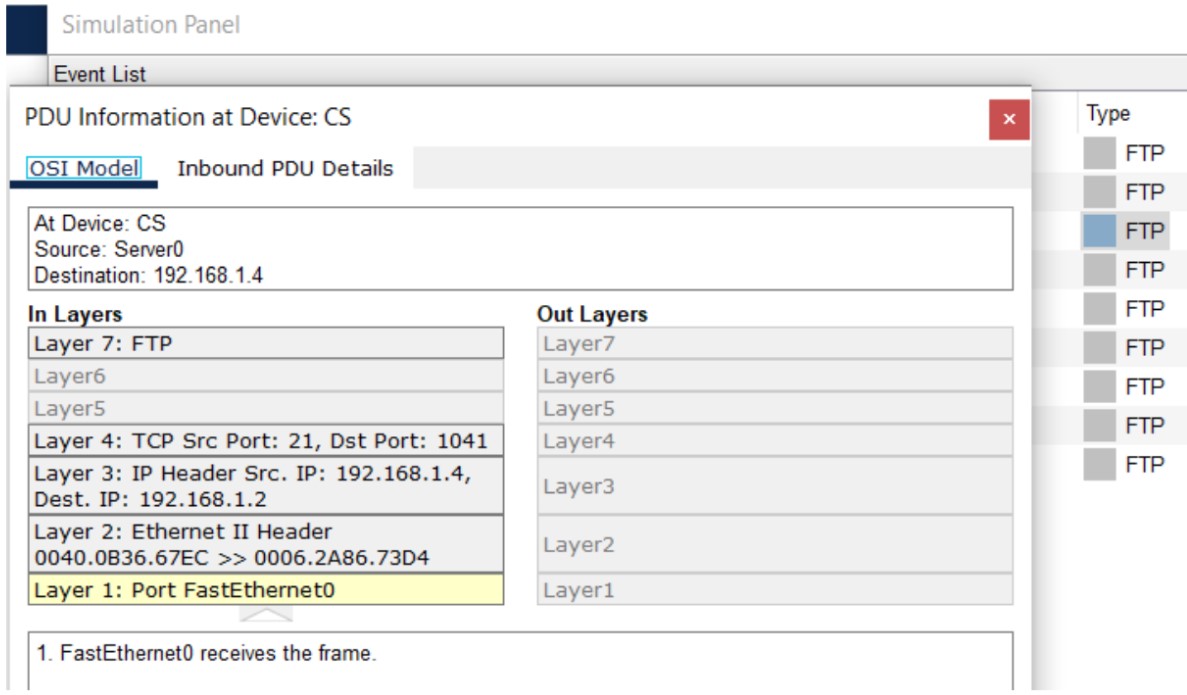
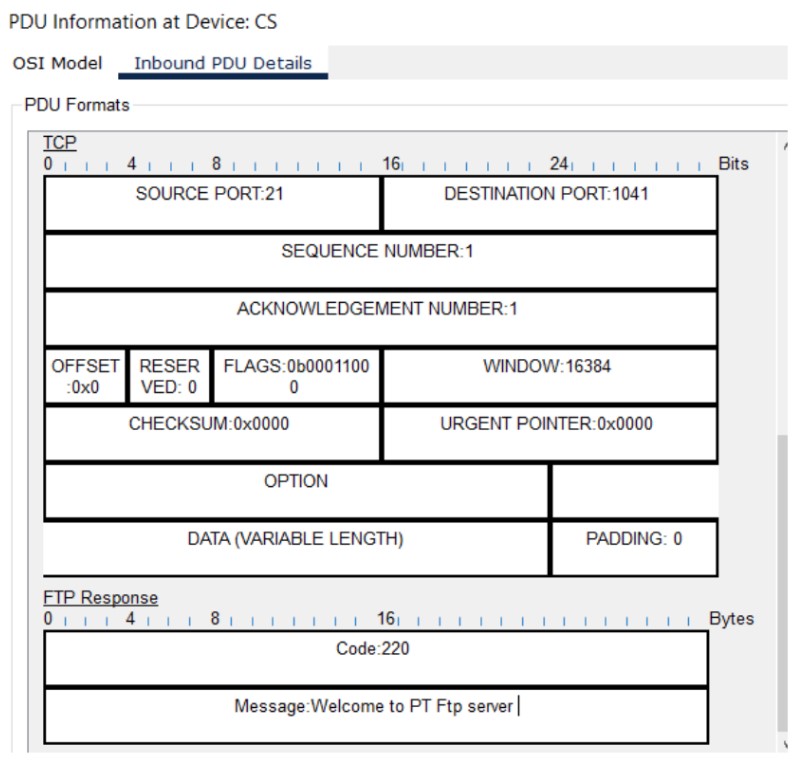
Figure 6: FTP implementation network topology with FTP server and client PCs.
# Wireshark HTTP Analysis Steps:
1. Start Wireshark capture
2. Enter "http" in display filter
3. Browse to: http://gaia.cs.umass.edu/wireshark-labs/HTTP-wireshark-file1.html
4. Stop capture and analyze GET/response messages
# DNS Analysis with nslookup and Wireshark:
1. Clear DNS cache: ipconfig /flushdns
2. Start Wireshark capture
3. Run: nslookup www.mit.edu
4. Analyze DNS query/response packets
5. Note: DNS uses UDP port 53
1. What ports does SMTP use for server-to-server and client-to-server communication?
2. Explain the purpose of POP3 in email systems.
3. What are the main SMTP commands and their functions?
1. Differentiate between FTP active and passive modes.
2. Why does FTP use separate control and data connections?
3. What security concerns exist with standard FTP?