

Network: System of interconnected devices or people.
Computer Network: Telecommunications network allowing devices to share data and resources via cables or wireless media.
Host: Any device (PC, server) connected to a network with a unique identifier (IP).
Topology: Arrangement of network elements (bus, ring, star, tree, mesh).
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| MAC | Physical address of a device |
| IP Address | Unique address assigned to host/router (e.g., 192.168.0.1) |
| Hub | A hub is a basic networking device that connects multiple devices in a LAN and operates at the physical layer. When a device sends data to the hub, it broadcasts the data to all connected devices, regardless of the intended recipient. Only the correct device processes the data, while others ignore it. |
| Port | 65,535 ports on host for different applications |
| Gateway | Router address connecting network to other networks |
| DNS Server | Converts domain names to IP addresses |
| DHCP | Dynamically assigns IPs and DNS addresses |
A 7-layer conceptual model standardizing how systems communicate.
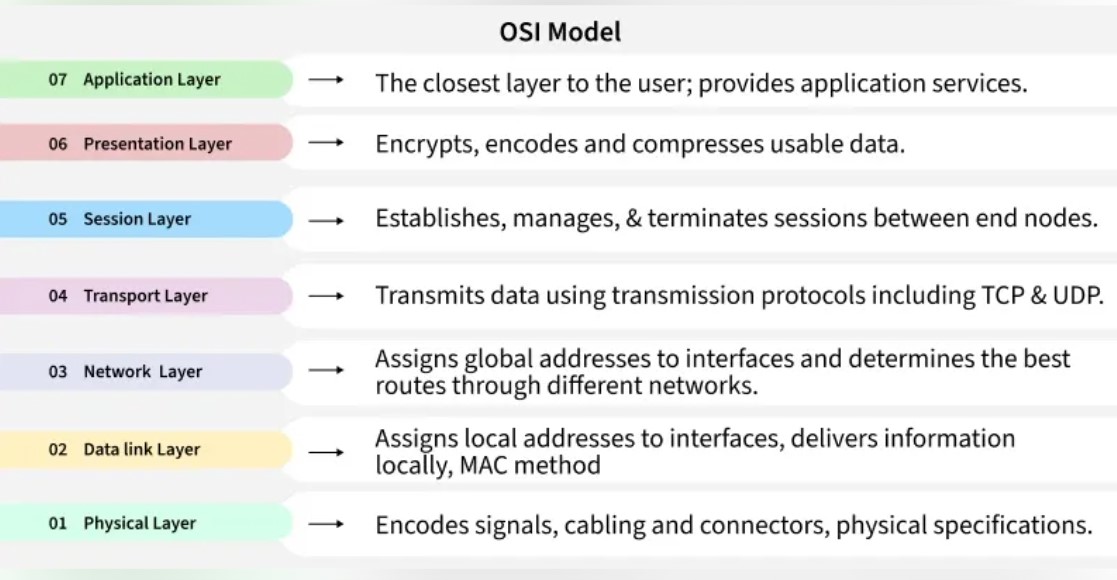
Figure 1: OSI Model – 7 Layer Architecture Overview
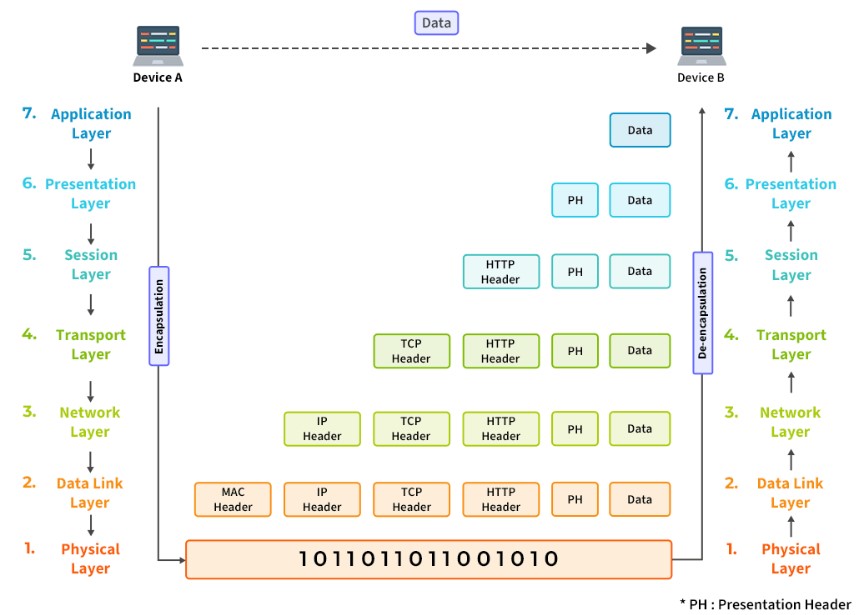
Figure 2:OSI Model and Headers at each stage.
IPv4 addresses divided into Class A, B, C for different network sizes.
Default subnet masks: all network bits set to 1, host bits set to 0 (no subnetting).
| Class | Range | Network ID | Host ID | Default Subnet Mask | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1.0.0.0 to 127.0.0.0 | First octet | Last three octets | 255.0.0.0 | Large networks |
| B | 128.0.0.0 to 191.255.0.0 | First two octets | Last two octets | 255.255.0.0 | Medium networks |
| C | 192.0.0.0 to 223.255.255.0 | First three octets | Last octet | 255.255.255.0 | Small networks |
| D | 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255 | N/A | N/A | N/A | Multicasting |
| E | 240.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255 | N/A | N/A | N/A | Experimental |
| Class | Private IP Range | Default Subnet Mask | Number of Networks | Number of Hosts per Network | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255 | 255.0.0.0 | 1 | 16,777,214 | Used for very large private networks |
| B | 172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255 | 255.255.0.0 | 16 | 65,534 | Used for medium-sized private networks |
| C | 192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255 | 255.255.255.0 | 256 | 254 | Used for small home or office networks |
These are essential Windows command-line tools that every IT or CS student should know. They are commonly used for network configuration, diagnostics, and analysis.
| Task | Command | Description / Purpose | Example Output / Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1) View IP configuration | ipconfig |
Displays the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway for all adapters. | Used to check current network configuration. |
| 2) View detailed IP configuration | ipconfig /all |
Shows full adapter info including MAC address, DHCP, and DNS details. | Used to get complete system network info. |
| 3) Display system hostname | hostname |
Displays the name of the computer on the network. | Used to identify the device. |
| 4) Check any one port on TCP (e.g., Port 80) | netstat -an | findstr ":80" |
Searches for active connections using TCP port 80. | Verifies if web service or HTTP port is active. |
| 5) Display number of datagrams sent and received | netstat -s |
Shows statistics for TCP, UDP, ICMP, and IP protocols. | Useful for analyzing packet transmission and errors. |
| 6) Display active network connections | netstat |
Lists all active TCP connections and listening ports. | Shows who your system is communicating with. |
| 7) Display all active connections with process IDs | netstat -ano |
Displays active connections along with their corresponding process IDs (PIDs). | Used to identify which application is using a port. |
| 8) Trace route to a destination | tracert <destination> |
Traces the path packets take to reach a host. | tracert google.com shows route hops to Google. |
| 9) Find all other hosts available on the network | arp -a |
Displays the ARP table mapping IP addresses to MAC addresses. | Lists devices currently communicating with your system. |
| 10) Find DNS information for a domain | nslookup <domain_name> |
Queries DNS to find the IP address or other DNS records of a domain. | Helps resolve domain names to IP addresses and troubleshoot DNS issues. |